Mastering CSS Syntax: A Beginner's Guide to Crafting Stylish Websites- w9school
Unlock the world of CSS syntax and create stunning websites with our beginner-friendly guide. Start your styling journey today!
CSS Syntax |
|
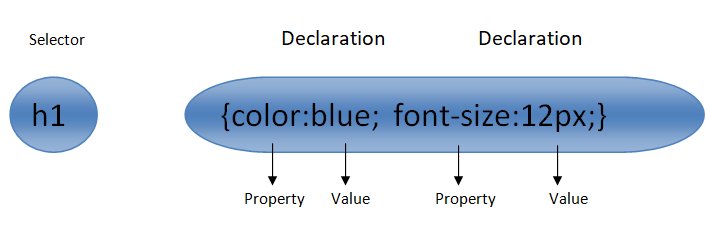
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) syntax defines how styles are written in CSS to control the presentation and layout of HTML or XML documents. CSS syntax consists of rulesets, declarations, selectors, properties, and values.CSS syntax is a set of rules that you have to follow whenever you are writing code in CSS. If you don't follow the syntax then the system will not run and apply the style on your webpage Here's an overview of each component of CSS syntax: 1- Ruleset: A ruleset is the fundamental building block of CSS and consists of a selector followed by a declaration block. It specifies which HTML elements the styles will apply to. 2- Selector: The selector targets HTML elements that you want to style. There are various types of selectors in CSS, including:
3- Declaration Block: The declaration block is a set of property-value pairs enclosed in curly braces 4- Property: The property represents a style attribute that you want to apply to the selected HTML elements. There are numerous CSS properties available, such as 5- Value: The value is the setting you assign to a property. It defines how the selected elements should appear according to the specified property. 6- Comments: You can add comments in CSS using CSS syntax allows you to define styles for various HTML elements, classes, and IDs, enabling you to create visually appealing and consistent layouts for web pages. These are the basic components of CSS syntax. By combining selectors, properties, and values, you can create various styles to control the appearance of your HTML elements on the web page. |
CSS Syntax Overview |
|
|
Example In this example all elements will be center-aligned, with a red text color:
Example Explained:
|
CSS Selectors |
|
A CSS selector selects the HTML element(s) you want to style. CSS Selectors CSS selectors are used to "find" (or select) the HTML elements you want to style.We can divide CSS selectors into five categories:
This page will explain the most basic CSS selectors.
Test Yourself with CSS ExercisesAre You Ready? If Yes! then Click Here |
What's Your Reaction?